A covered call Strategy is a selection plan that deals with ownership of the primary benefit as well as a selective agreement on the underlying. The broker has a great place in security, and simultaneously, he writes a call option on the same protection to make a profit through Premium.
Covered Call Trading Strategy
The covered call Strategy plan performs excellently when the broker is light-hearted towards the market. He knows that he cannot create good revenue just by having a primary asset. Therefore, he sells call options on security, at a higher raid price, and gets a premium until prices reach that point. The strategy offers limited profit to the broker, but the loss can be unlimited as the broker has not secured himself against the lowering price movement.
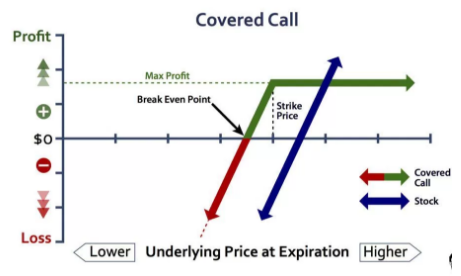
So, this plan must be used very carefully, and only if the broker is sure that there will not be many movements in price. Thus, to generate a covered call trade, the trader must buy or own a specific number of shares and then trade an out-of-the-money call option for a similar figure of shares at a higher strike cost. The broker then waits for the call option to either get practice or end. If it ends, the broker receives back his shares and also receives a consistent return through the premiums till to finish.
COVERED CALL OPTION TIME
The best time to use a covered call option plan is when the shareholder is mere somewhat optimistic or market neutral. He hopes prices to rise and fall sharply. Without the rise in the cost of the essential asset, he can still control to generate steady revenue from his acquisitions by writing a call option on the security and getting premiums. Such a plan is not appropriate in situations when the shareholder is inclined towards the market very fast. If he hopes the cost to rise sharply, he is happier, just holding the essential asset. In such situations, he will earn due to the increase in price, and his income will not be restricted affected by the call option.
\When the shareholder is a trader who is suffering from a sharp fall in asset prices, he will have to avoid losses by selling the stock instead of writing a call option. If the price is down too much, the Premium earned will not be sufficient to pay off for the loss on the stock. The highest revenue in the covered call plan is limited to the difference between the strike cost of the call option and the buying cost of the basic plus the premiums earned from trading the call option. The most significant loss in this plan is unlimited. It depends on the value of the essential asset. The only savior is the Premium earned on trading the call option.
COVERED CALL WRITING
When someone says they want to proceed with Covered call writing, it means that they are currently trying to sell their right to buy a stock. We can see that you have 100 shares of Infosys, and you are not very happy about this specific supply in the upcoming days. Such a condition offers you the opportunity to write the cost on the shares of Infosys, which is appropriate for the expiration date of your closest choice. You will get receive a premium for placing a covered call in writing. But when you set a premium cost and select an ending date, confirm to have a quick look at what’s occurring around the stock industry domestically and globally.
Moreover, also be attentive for all contracts, acquisitions, strategies being announced not only by the company but also by its nearest rivals.
COVERED CALL PAYOFF
When it comes to down for you to calculate payments by covered call Strategy, you have to be attentive about some variables to come down in numbers. At first, you have to calculate the cost of the covered call that is equal to the difference between the value of the primary advantage at the practice date and the amount above zero and the difference between the value of the asset at practice date and the practice cost. These values can be concluded with the support of a couple of paragraphs.
COVERED CALL FORMULA
You can easily calculate it as:
CCV=PU-MAX [0 or PU-EP]
where,
CCV: Covered Call Value
PU: Price of the underlying benefit of the practice date
EP: Exercise Price
now calculating the revenue from this covered
Calculating that value is an additional room for the above calculation.
Profit = CCV- PS + Premium
where,
PS: is the price of the asset at the beginning of the plan, and certainly, Premium is the price compensated by the purchaser to the covered call seller/writer.
COVERED CALL RETURNS
You have to use different calculated formulas for the full purpose of your threats and returns.
To cover call profits;
Returns = (Income/investment) X Time
Now, when you separate these entitles down, and then you can see the revenue as the total of the Call option and dividend received if the latter exists. Moreover, the time factor will be the sum of the days in a year dividend by the days you are left with before the call ends. For example, ICICI bank share value 1000 had a call value 10 with 60 days left for an agreement to be ended. There was a dividend of 1 stated by the company too.
Put all values into the formula,
= (10+1)/100X365/60
= 0.67 or 67%
COVERED CALL RISK
The only downside to a covered call Strategy is the reverse loss.
It means that “if the stock value gets higher, it will be more moderate or neutral than your starting ideas.” In such situations, you will miss out on the chances to sell the stock at the current high price, and you will have to stick with the strike price and your default premium. However, the stock price may be lower or maybe a little higher than what you do in this deal
COVERED CALL DIVIDEND
When dividend things in a skillful manner in a covered call option mean to pinch the strike values, the option price, and the matching stock instability. The price of a guaranteed stock is comparatively down. This is offset by the Premium paid, and such stock is then seen as a safe bet. When safety is enhanced, stock instability is reduced and, thus, the enjoyment of high-risk revenue is eliminated.
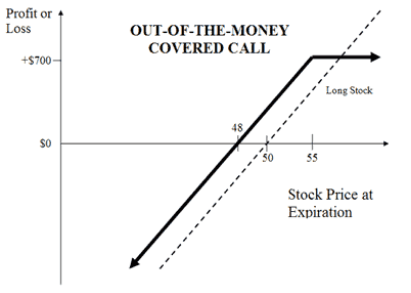
COVERED CALL EXAMPLE
To understand it lets suppose that a dealer owns 100 shares of Adani Power that are presently at a market price of 5O each. The trader does not wait for the prices to rise sharply. Therefore, to create stable revenue, he trades a call option with a hit price of 55 for the 100 shares. The Premium earned for a trading call option is 2 per share that becomes 2OO in total.
SCENARIO 1
When the values of the shares of Adani Power increases to 757 per share, the call option will be used when the share price exceeds the call strike price. The total profit will be (5755)*1 00= 7200.
The Premium received will be 2*100= 1200.
Thus, the net payoff will be 200+200= 1400.
If the covered call was not generated, the dealer could get a revenue of (5750)*100= 7700.
SCENARIO 2
If the price of the shares increases up to 754 per share, the call option will not be used. The dealer will get a revenue of (54S0)*100= Rs 400, in addition to a premium of 7200.
The net payoff will be 400+200= 7600.
Now, if the covered call was not generated, the revenue would have been just (5450)*100= 7400.
SCENARIO 3
If the stock revenue of Adani Power decreases to 4O, the dealer will lay himself open to a loss. The total loss is equal to (5O40)*1 00= 1OOO.
After winning the Premium from the call option, the net risk is decreased to 1000-200= 8OO.
COVERED CALL ADVANTAGES
- The plan supports to create consistent revenue from an asset that would not otherwise be profitable due to the inefficiency of instability in the market.
- The dealer can take advantage of the fluctuations in stock prices
COVERED CALL DISADVANTAGES
- The plan has several threat potentials.
- The revenue is restricted due to the use of a covered call.
CONCLUSION
As a result, the covered call plan is a hazardous policy and should be applied just when the dealer is convinced that there will be no harm to the price of the underlying asset.
On the other hand, if the price goes down, the plan cannot secure against the risks. That’s why it is mandatory to perform with stocks that have average indirect instability. One needs to get ready to face every emergency and have a clear vision of the investment.
Also learn Arbitrage Forex Trading strategy



